Rihla (The Journey) – was the short title of a 14th Century (1355 CE)
book written in Fez by the Islamic legal scholar Ibn Jazayy al-Kalbi of Granada
who recorded and then transcribed the dictated travelogue of the Tangerian, Ibn
Battuta. The book’s full title was A Gift
to Those who Contemplate the Wonders of Cities and the Marvels of Travelling
and somehow the title of Ibn Jazayy's book captures the ethos of many of the
city and country journeys I have been lucky to take in past years.
This rihla
is about Chaldiran in NW Iran.
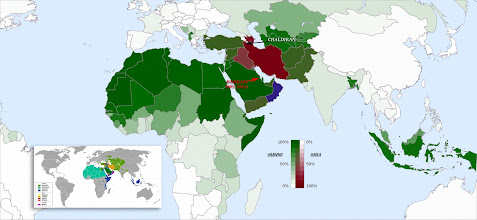
DISTRIBUTION OF SUNNI AND SHIA BRANCHES OF ISLAM
'Bahrain’s highest court has upheld jail terms
issued against nine medics – including Irish-trained orthopaedic surgeon Ali
al-Ekry – convicted for their role in last year’s pro-democracy uprising, state
news agency BNA reported. The controversial case has drawn international
criticism of the US-allied Gulf Arab kingdom, which has been in turmoil since
the protests led by its Shia Muslim majority were crushed by the Sunni rulers. Bahrain,
home base for the US navy’s fifth fleet, accuses regional Shia power Iran of
encouraging the unrest and has promised a tough response to violent protests as
talks with the opposition have stalled.'
Irish Times 2nd
October 2012
Throughout the Middle East and North Africa over the
past two years the so-called Arab Spring has seen in a parallel development to secular
demands for greater democracy an opportunist and orchestrated acceleration of
fundamentalist Sunni neo-militarism, funded in the main by Saudi Arabian based organisations, to fill the political and religious vacuums created by regime
implosions. To a great extent this Sunni militarism has focused on internal
control of faith and power (with occasional diversionary mob incitement against
western interests for such things as the publication of cartoons deemed
offensive) but where there is an obvious Shia opposition or power base such as
in Syria with the ruling Alawis, against the Houthis in Yemen, or as outlined
above in Bahrain then the Sunni efforts to eradicate Shia influence have become
most determined. This on-going schism amongst Muslims has led to atrocities
being perpetrated by both sides in a complete denial of what true Islam
purports to be.
And when blame is being apportioned where else does
Sunni wrath turn, to create a demonised target (and in the cynical way of
real-politic incite or be duped by the involvement of Israel and the
American-Israeli caucus) but to the dominant Shia entity that is the Islamic
Republic of Iran.
VALLEY OF CHALDIRAN LOOKING NORTHWEST
In nearly 1400 years from the time of the first
Islamic civil war (First Fitna 656-661 C.E.) the Sunni-Shia internecine
struggle for the control of power and faith in Islam (between Arabia and Iran)
has not changed much but one of its most violent expressions occurred at the
Battle of Chaldiran, in present day North Western Iran on 23 August 1514 when
approximately 7000 (2000 Ottoman Sunni and 5000 Safavid Shia) died defending
their version of faith in addition to a pre-emptive genocide of about 40,000
Anatolian Shia by the Sunni Ottomans in advance of the battle.
I like travelling in places where there are land
borders between states. In some instances the geography of that separation can
be as great as a high mountain range or as puny as a trickling stream. Frontier
people are different: equally accommodating or equally suspicious in two or
three languages, two political rhetoric’s, two legislative structures, two
religions, or two or more versions of the truth and very often as a family, a
clan or a tribe will straddle the divide. At frontiers your senses become
alive, alert to nuances that elsewhere become mundane.
ISHAK PASHA PALACE DOGUBAYAZIT, TURKEY LOOKING NORTH
In October 2008 while travelling in Eastern Turkey I made my way to
Dogubayazit, a large city about 35km from the Turkish-Iranian border. It sits
in a green valley in the lee of snow-capped Mount Ararat (known by the Arabs as Jabal al-ārith, by the
Turks as Büyük Aǧrı Daǧ, by the Iranians as Kūh-i Nū_ (Mountain of Noah) and
as Mount Masis, or Masik, by the Armenians) and spent the
morning dodging Turkish soldiers and Kurdish vendors on very dusty streets. Later on a balmy afternoon I sat
on the terrace of the small restaurant that overlooks the magnificent palace
fortress of Ishak Pasha, which is built on a high valley buff that stands
sentinel over Dogubayazit from the south. To the east and against the valley
wall were the ruined walls of an Urartu fortress and a small mosque. A man
beside me watched me take photographs and then he introduced himself. He was a
Kurd, from Diyarbakir, a lawyer educated in Paris and London, in Dogubayazit
representing some local men who had been rounded up in a recent Turkish
crackdown on Kurdish secessionism. He pointed to the small mosque and told me
it had been commissioned by the Ottoman Sultan, Selim I, known as The Grim, on
his way to a place called Chaldiran, which lay about 70km to the south-east in
Iran. The Battle of Chaldiran, he told
me was not only a dogma defeat for the Shia Iranians by the Sunni Ottomans but
also was responsible for splitting the Kurdish homelands into two halves of
influence, a situation which has existed to this day.
Selim I, Yavuz Sultan Selim Khan (Yavuz means steadfast but was often
translated in English as the Grim) came to the Ottoman throne in 1512 CE.
Having battled and then forced the abdication of his father Bayazit II he
subsequently defeated and then killed his rivals for the throne, his brother Ahmet
in April 1513 as well as his other brother Korkut and nephews, thereby
eradicating all internal opposition. He then turned his attentions to the east
where the opposition was of a greater danger to his authority, his sultanship.
Shah Ismail I, founder of the Safavid dynasty, was
the last of the hereditary masters of the Safaviyya Sufi order. His father had
mobilized Turkomen tribes into militant Qizilbash ( ‘Red Heads’ so-called from
the red peaks to their turbans and the 12 perforations denoting the 12 Imams of
Twelver Shiism) groups. In 1501 Ismail with the support of the Qizilbash troops
was crowned Shah of Azerbaijan and by 1510 Shah of Iran. On accession to power
he declared Shi’sm to be the State Religion and began dispatching Qizilbash
missionaries deep into the heart of Ottoman Anatolia (where in 1511 they
orchestrated a revolt against Bayazit II that eventually signalled his
downfall). In addition he advanced his forces as far as present day Diyarbakir
and southern Iraq. His ascension, and the ascension of a Shia state posed a
direct threat to Ottoman religious and temporal authority.
Selim I, in response, gathered an army of 140,00 and
force-marched it from Sivas in central turkey to Dogubayazit and then upwards
to the high valley of Chaldiran where an army of about 40,000 Qizilbash troops
under Ismail I had gathered. In 1511 following the suppression of the Qizilbash
Turkomen-Alevi Kurd Shia Shakulu uprising 40,000 Shia were exterminated and to
ensure that no further Shia remained behind his army to cause trouble Selim had
ordered Yunus Pasha, before setting out on campaign, to supervise the inquisition
and massacre of all Shia in his dominions. This distrust of Alevism still
exists in Turkey today.
‘Then, with the support and
assistance of God, I will crown the head of every gallows tree with the head of
a crown-wearing Sufi and clear that faction from the face of the earth .... and
maneuvering in accordance with “Put them to death wherever you find them” (Qur’an
4: 89), will wreak ruin upon you and drive you from that land.’
Selim I
In advance of the armies meeting Selim and Ismail had
exchanged diplomatic correspondence. Ismail dictated his in Azerbaijani Turkish,
which was the language of his people and of his powerbase. Selim on the other hand
replied in Persian, which he knew Ismail did not have a full grasp of. They
insulted each other by referring to each other’s addictions. In Ismail’s case
it was his liking for alcohol and in Selim’s case for opium. Indeed in the
final communication before the battle Ismail sent an ambassador, Shah Quli Aga
with a golden casket full of opium for Selim with the request that no harm come
to the ambassador.
‘Bitter experience has taught
that in this world of trial
He who falls upon the house of ‘Ali always falls.
Kindly give our ambassador leave to travel unmolested for “No soul shall bear
another’s burden.” (Qur’an 6: 164; 53: 38) When war becomes inevitable,
hesitation and delay must be set aside, and one must think on that which is to
come. Farewell.’
Ismail I
Selim had Quli Aga executed for the insult on the
spot!
THE BATTLE OF CHALDIRAN 23 AUG 1514
TROOP DEPLOYMENTS
Around the 23 August 1514CE Sultan Selim’s troops
entered into the valley of Chaldiran from the north. Knowing that they were
heavily outnumbered some of Ismail’s commanders requested that they attack
immediately before the Ottoman army had a chance to fully deploy. In the centre
of the Ottoman forces were cannon batteries and a battalion of crack Janissary
troops. Ismail refused, believing in his own sense of invincibility and also an
archaic code of chivalry. Ismail’s forces did not have cannon ( a mistake they
never made again) and on the morning of the 23 August 1514 his cavalry began to
attack the Ottoman flanks. The ottoman artillery decimated them and the Safavid
army was driven from the valley with 7-10,000 dead and leaving behind one if
not two of Ismail’s wives who were subsequently married off to Ottoman
generals.
There are two other interesting asides to the battle.
Firstly Selim entered Tabriz, the Safavid capital,
and wanted to pursue the retreating Ismail towards the Caspian but was
dissuaded by his Janissary commanders who partially revolted, explaining that
because of Ismail’s scorched earth policy in eastern Anatolia the army could
not be kept supplied. Although the Janissary troops loved their food it is
possible that the hesitation on their parts was that the Janissaries were
closely allied to the Becktasi Sufi Order a very similar order to that of
Ismail’s Safaviyya and may not wanted to pursue their co-Sufi.
Secondly in a positive development Ismail’s empire
was noted for its Timurid inspired artists and calligraphers and upwards of
1000 artisans from the Safavid dominions were transported back to Istanbul
where they provided the fundamental spark to the subsequent flowering of the
high period of Ottoman art.
On St Patrick’s Day, the 17th March 2009,
I travelled up from Tabriz in NW Iran to see the battlefield and valley of
Chaldiran for myself. Approaching from the south-east having first stopped at St
Thaddeus Monastery and Qara Church the sense of theatre could not be dismissed.
A bitter-cold wind whipped in from the east. Snow-capped mountains rising to
2600m surrounded a fertile plain which is at 1820m above sea level with a
single natural exit point to the north and to the south. There is a battlefield
memorial between the villages of Sa’dal and Gal Ashaqi on the western rim of
the valley.
Chaldiran is a Coliseum on a grand scale, a killing
zone where Sunni and Shia exterminated each other in the name of faith and
power and left a legacy that resonates to this day.
The silent screams deafened, as they now do in
Aleppo, Syria and Manama, Bahrain.